基础:如何用MATLAB生成AWGN噪声?(附源代码)
MATLAB中的help文档,是一个神奇的存在,检索你想找的关键词,会自动检索出与关键词相关的内容。例如:检索一下“awgn”,我们可以得到如下图所示的界面。
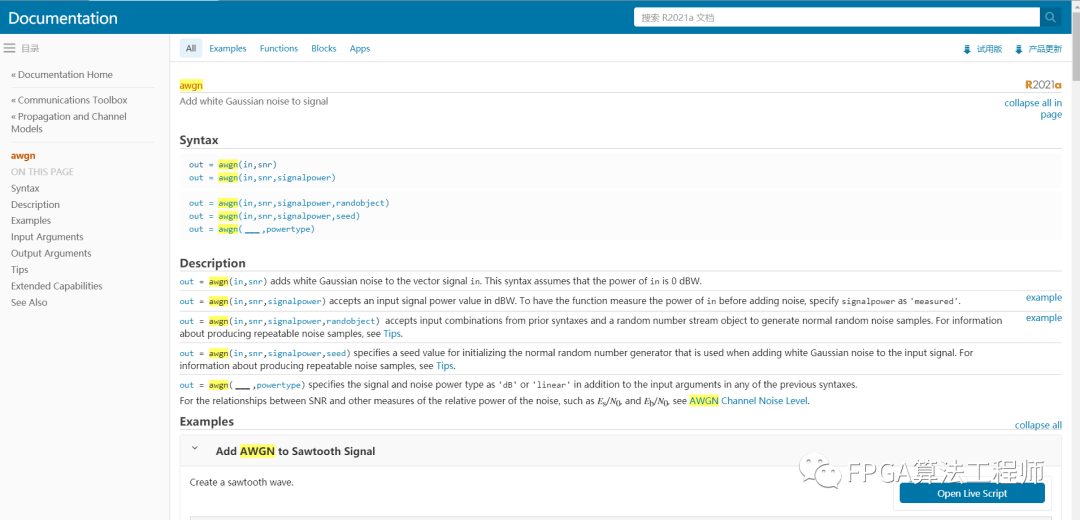
可以非常方便地查阅函数的语法定义,信号定义,以及给出example。
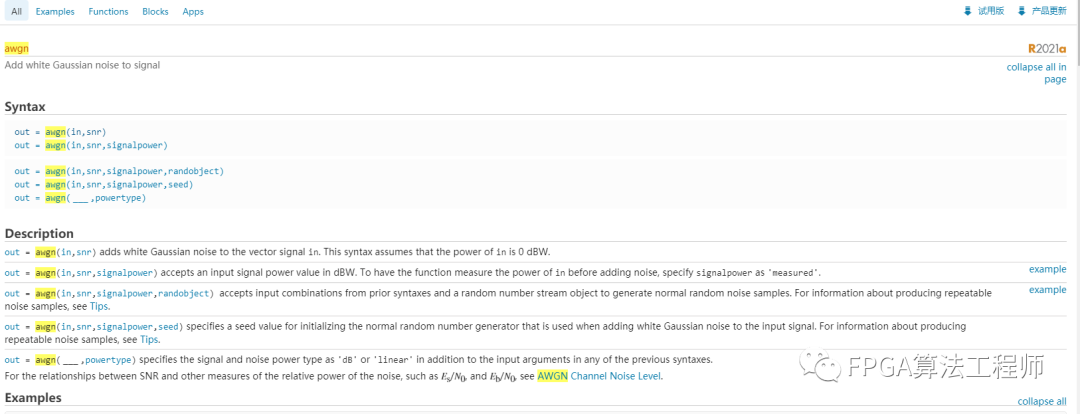

大部分非核心函数,可以打开看到源码,例如awgn的源码:
function y = awgn(varargin)
%AWGN Add white Gaussian noise to a signal.
% Y = AWGN(X,SNR) adds white Gaussian noise to X. The SNR is in dB.
% The power of X is assumed to be 0 dBW. If X is complex, then
% AWGN adds complex noise.
%
% Y = AWGN(X,SNR,SIGPOWER) when SIGPOWER is numeric, it represents
% the signal power in dBW. When SIGPOWER is 'measured', AWGN measures
% the signal power before adding noise.
%
% Y = AWGN(X,SNR,SIGPOWER,S) uses S to generate random noise samples with
% the RANDN function. S can be a random number stream specified by
% RandStream. S can also be an integer, which seeds a random number
% stream inside the AWGN function. If you want to generate repeatable
% noise samples, then either reset the random stream input before calling
% AWGN or use the same seed input.
%
% Y = AWGN(..., POWERTYPE) specifies the units of SNR and SIGPOWER.
% POWERTYPE can be 'db' or 'linear'. If POWERTYPE is 'db', then SNR
% is measured in dB and SIGPOWER is measured in dBW. If POWERTYPE is
% 'linear', then SNR is measured as a ratio and SIGPOWER is measured
% in Watts.
%
% Example 1:
% % To specify the power of X to be 0 dBW and add noise to produce
% % an SNR of 10dB, use:
% X = sqrt(2)*sin(0:pi/8:6*pi);% Y = awgn(X,10,0);
%
% Example 2:
% % To specify the power of X to be 3 Watts and add noise to
% % produce a linear SNR of 4, use:
% X = sqrt(2)*sin(0:pi/8:6*pi);
% Y = awgn(X,4,3,'linear');
%
% Example 3:
% % To cause AWGN to measure the power of X and add noise to
% % produce a linear SNR of 4, use:
% X = sqrt(2)*sin(0:pi/8:6*pi);
% Y = awgn(X,4,'measured','linear');
%
% Example 4:
% % To specify the power of X to be 0 dBW, add noise to produce
% % an SNR of 10dB, and utilize a local random stream, use:
% S = RandStream('mt19937ar','Seed',5489);
% X = sqrt(2)*sin(0:pi/8:6*pi);
% Y = awgn(X,10,0,S);
%
% Example 5:
% % To specify the power of X to be 0 dBW, add noise to produce
% % an SNR of 10dB, and produce reproducible results, use:
% reset(RandStream.getGlobalStream)
% X = sqrt(2)*sin(0:pi/8:6*pi);
% Y = awgn(X,10,0);
%
%
% See also comm.AWGNChannel, WGN, RANDN, RandStream/RANDN, and BSC.
% Copyright 1996-2018 The MathWorks, Inc.
%#codegen
narginchk(2,5);
% Validate signal input
sig = varargin{1};
validateattributes(sig, {'numeric'}, ...
{'nonempty'}, 'awgn', 'signal input');
% Validate SNR input
reqSNR = varargin{2};
validateattributes(reqSNR, {'numeric'}, ...
{'real','scalar','nonempty'}, 'awgn', 'SNR input');
% Validate signal power
if nargin >= 3
if strcmpi(varargin{3}, 'measured')
sigPower = sum(abs(sig(:)).^2)/numel(sig);
% linear
else
validateattributes(varargin{3}, {'numeric'}, ...
{'real','scalar','nonempty'}, 'awgn', 'signal power input');
sigPower = varargin{3}; % linear or dB
end
else
sigPower = 1; % linear, default
end
% Validate state or power type
if nargin >= 4
coder.internal.errorIf(comm.internal.utilities.isCharOrStringScalar(varargin{4}) && ...
all(~strcmpi(varargin{4}, {'db','linear'})), ...
'comm:awgn:InvalidPowerType');
isStream = ~isempty(varargin{4}) && ~comm.internal.utilities.isCharOrStringScalar(varargin{4});
if isStream && ~isa(varargin{4}, 'RandStream') % Random stream seed
validateattributes(varargin{4}, {'double'}, ...
{'real','scalar','nonnegative','integer','<',2^32}, ...
'awgn', 'seed input');
end
else % Default
isStream = false;
end
% Validate power type
if nargin == 5
coder.internal.errorIf(comm.internal.utilities.isCharOrStringScalar(varargin{4}), ... % Type has been specified as the 4th input
'comm:awgn:InputAfterPowerType');
coder.internal.errorIf(all(~strcmpi(varargin{5}, {'db','linear'})), ...
'comm:awgn:InvalidPowerType');
end
isLinearScale = ((nargin == 4) && ~isStream && strcmpi(varargin{4}, 'linear')) || ...
((nargin == 5) && strcmpi(varargin{5}, 'linear'));
% Cross-validation
coder.internal.errorIf(isLinearScale && (sigPower < 0), ...
'comm:awgn:InvalidSigPowerForLinearMode');
coder.internal.errorIf(isLinearScale && (reqSNR < 0), ...
'comm:awgn:InvalidSNRForLinearMode');
if ~isLinearScale % Convert signal power and SNR to linear scale
if (nargin >= 3) && ~comm.internal.utilities.isCharOrStringScalar(varargin{3}) % User-specified signal power
sigPower = 10^(sigPower/10); end reqSNR = 10^(reqSNR/10);
end
noisePower = sigPower/reqSNR;
if isStream
if isa(varargin{4}, 'RandStream')
stream = varargin{4};
elseif isempty(coder.target)
stream = RandStream('shr3cong', 'Seed', varargin{4});
else
stream = coder.internal.RandStream('shr3cong', 'Seed', varargin{4});
end
if ~isreal(sig)
noise = sqrt(noisePower/2)* (randn(stream, size(sig)) + ... 1i*randn(stream, size(sig)));
else
noise = sqrt(noisePower)* randn(stream, size(sig));
end
else
if ~isreal(sig)
noise = sqrt(noisePower/2)* (randn(size(sig)) + 1i*randn(size(sig)));
else
noise = sqrt(noisePower)* randn(size(sig));
end
end
y = sig + noise;
% [EOF]
但是,如果不用MATLAB内置的awgn函数,如何用MATLAB生成AWGN噪声?
可以自己写一个,可以找找别人写的,站在别人的肩膀上,可以看得更远。(如果是学习,建议理解awgn背后的原理和定义,然后自己写;如果只是为了应用,提高效率,直接用,浮躁的沉不下来的心,已经蔓延~)
下面这份文档,借花献佛,在不用内置的函数下,用MATLAB生成AWGN噪声,可以参考一下。





文档来源于https://www.gaussianwaves.com,国外的网站,总是这么专业!
高斯波形,信号处理,通信系统,简洁明了。



MATLAB 源码:
%author - Mathuranathan Viswanathan (gaussianwaves.com
%This code is part of the books: Wireless communication systems using Matlab & Digital modulations using Matlab.
function [r,n,N0] = add_awgn_noise(s,SNRdB,L)
%Function to add AWGN to the given signal
%[r,n,N0]= add_awgn_noise(s,SNRdB) adds AWGN noise vector to signal
%'s' to generate a %resulting signal vector 'r' of specified SNR
%in dB. It also returns the noise vector 'n' that is added to the
%signal 's' and the spectral density N0 of noise added
%
%[r,n,N0]= add_awgn_noise(s,SNRdB,L) adds AWGN noise vector to
%signal 's' to generate a resulting signal vector 'r' of specified
%SNR in dB. The parameter 'L' specifies the oversampling ratio used
%in the system (for waveform simulation). It also returns the noise
%vector 'n' that is added to the signal 's' and the spectral
%density N0 of noise added
s_temp=s;
if iscolumn(s), s=s.'; end; %to return the result in same dim as 's'
gamma = 10?(SNRdB/10); %SNR to linear scale
if nargin==2, L=1; end %if third argument is not given, set it to 1
if isvector(s),
P=L*sum(abs(s).?2)/length(s);%Actual power in the vector
else %for multi-dimensional signals like MFSK
P=L*sum(sum(abs(s).?2))/length(s); %if s is a matrix [MxN]
end
N0=P/gamma; %Find the noise spectral density
if(isreal(s)),
n = sqrt(N0/2)*randn(size(s));%computed noise
else
n = sqrt(N0/2)*(randn(size(s))+1i*randn(size(s)));%computed noise
end
r = s + n; %received signal
if iscolumn(s_temp), r=r.'; end;%return r in original format as s
end
---END---
原文标题 : 基础:如何用MATLAB生成AWGN噪声?(附源代码)

最新活动更多
-
3月27日立即报名>> 【工程师系列】汽车电子技术在线大会
-
精彩回顾立即查看>> 【在线会议】汽车腐蚀及防护的多物理场仿真
-
精彩回顾立即查看>> 【在线会议】汽车检测的最佳选择看这里
-
精彩回顾立即查看>> 2024工程师系列—工业电子技术在线会议
-
精彩回顾立即查看>> 【线下论坛】华邦电子与莱迪思联合技术论坛
-
精彩回顾立即查看>> 【线下论坛】华邦电子与恩智浦联合技术论坛
推荐专题
- 1 七彩虹隐星P16 Pro首发评测
- 2 NVIDIA RTX 5060 Ti首发评测:8GB疯狂爆显存 16GB正好
- 3 华硕无畏Pro14酷睿版2025笔记本评测
- 4 完全的碾压性优势!锐龙9 9950X3D网游性能测试
- 5 索泰RTX 5070 XGAMING OC显卡评测
- 6 立讯精密得扛住苹果这波压力
- 7 Intel酷睿Ultra 285H体验DeepSeek 14B模型
- 8 联想卖爆了,但跟AI没啥关系
- 9 锐龙5 9600X搭配RX 9070 XT游戏测试:直接秒了Intel两代
- 10 DLSS 4小钢炮:微星GeForce RTX 5060 Ti 16G INSPIRE 2X首发评测





 分享
分享
















发表评论
请输入评论内容...
请输入评论/评论长度6~500个字
暂无评论
暂无评论